The Motion Gravity
The theory of motion gravity and complete proof based on the theory of general relativityThe Motion Gravity
The theory of motion gravity and complete proof based on the theory of general relativityThe introduction of three main structures for the stability of galaxies based on the theory of motion gravity
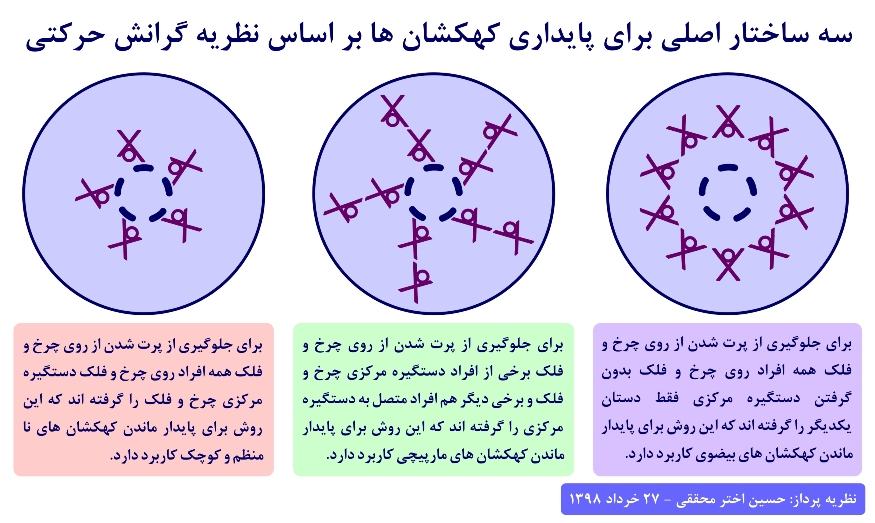
The theory of motion gravity and complete proof based on the theory of general relativity
According to the gravitational view of Einstein's general relativity, the Sun, for example, affects the context of space and time around itself, entails the introduction of gravitational gravitational forces on the earth, and thus floating the Earth's motion in its orbit around the sun, so if we assume In one moment, the sun disappears completely. According to Newton's gravitational view of the earth, at the instant the disappearance of the sun has been affected by the effects of the gravitational absence of the sun, and as a result, the earth immediately diverges from its orbit and goes out, but according to the gravitational view Einstein's General Relativity, which many experiments and observations have already confirmed Because the force of gravity of the sun relative to the Earth results from the presence of a gravitational swing from the sun that is approximately equal to the velocity of light in the vacuum and its effect on the space and time, hence, from the time of the disappearance of the sun until the fading effect The effect of the force of the gravitational acceleration of the sun on the Earth will take about a little more than eight minutes, which is equal to the time of sunlight coming to Earth. According to the views expressed by Newton and Einstein on the topic of gravity, a new theory, called the theory of gravity, is formed by correctly understanding the basis of the Newtonian General Gravitation Equation and the predicted gravitational waves Einstein introduces a new and more thorough view and equations for calculating the force of gravitational acceleration, and they answer many of the questions and ambiguities posed by cosmology and provide predictions in this area.
A projection of the main equation for calculation of force on objects in the theory of motion gravity:

Description of the theory of motion gravity:
As you can see in the figure below, if we have four points A and B, and C and D on a straight line in space, so that the distance between each of these points is, for example, equal to 300 million meters, or in other words Equal to X, or the same distance as light can travel in a vacuum in one second, as well as massively massive bodies with mass equal to each other, with the names M1, M2 and M3, respectively M1 at point C and M2 are placed on the point A and M3 on the point B. Therefore, without considering the effects of gravitational force between the two objects M2 and M3, we will see that, based on the gravitational view of general relativity Man T = 0 A gravitational wave of a body M1 released at space T at a time C at time C, and this wave, up to the point B, must be a distance equal to X, or about 300 millimeters, until T = 1 means that it is equivalent to one second and will affect the space and time around the point B and, as a result, add some gravitational acceleration force, called F3, onto the object M3, and also the gravitational wave to reach point A must be a distance equal to 2 * X or In the sense of about 600 million meters by T = 2, that is, equivalent to two seconds from the moment of propagation in space, and affect the space and time around the point A, and as a result, the gravitational acceleration force Inserting less force than gravitational acceleration F3, called F2, onto M2.
So far, everything goes well, but if we assume that at a time interval T = 0 to T = 1, when the gravitational wave extends from point C to the point B, the object M1, with the same velocity of propagation of gravitational waves from point C to The point D moves, so that after about one second, when the gravitational waves reach point B, the object M1 also reaches the point D, which, according to the gravitational view of the Einstein theory of relativity at the moment T = 1, again as when The object M1 remained constant at the same point C. The gravitational acceleration on the body M3 was constant due to the curvature of these gravitational waves on the structure of space and time around the point B, The M1 object after wave of gravitational emission in space does not affect its quality, and these waves behave independently, but the main thing is that if, at the same time as the object M1 moves from point C to point D, the object M2 With the same velocity, gravitational waves move from point A to point B, so after one second, at time T = 1, the object M1 reaches point D and the object M2 to point B, as well as gravitational waves, reach point B. In The result of the M2 object, like the M3 object, will receive the same gravitational effects that are generated by the emission of gravitational waves generated by the body M1, called the gravitational acceleration force F3, and the more important is that the Fa The crush of two objects M1 and M2 remains the same, and at both times T = 0 and T = 1, the distance between them is 2 * X, which is equivalent to six hundred million meters, while in this case, the state of the two M1 and M2 objects in One moves direction. The body M2 receives more gravitational acceleration, called F3, from the body M1, while in the case of the two bodies M1 and M2 being stationary, this gravitational gravitational force decreases to a lesser gravitational force F2.
Therefore, by moving two objects at a velocity and in the same direction, maintaining the distance between the two objects, we observe that the gravitational acceleration of the body is much faster than the oblique object, the body M1, on the object M2, and the interesting According to Einstein's general theory of general relativity, gravitational waves with the curvature of space and time give rise to a gravitational acceleration in bodies, therefore, it should be expected that the interacting force of the gravitational acceleration of the object is more rearward than the object In the foreground, the M2 object is reduced to M1.
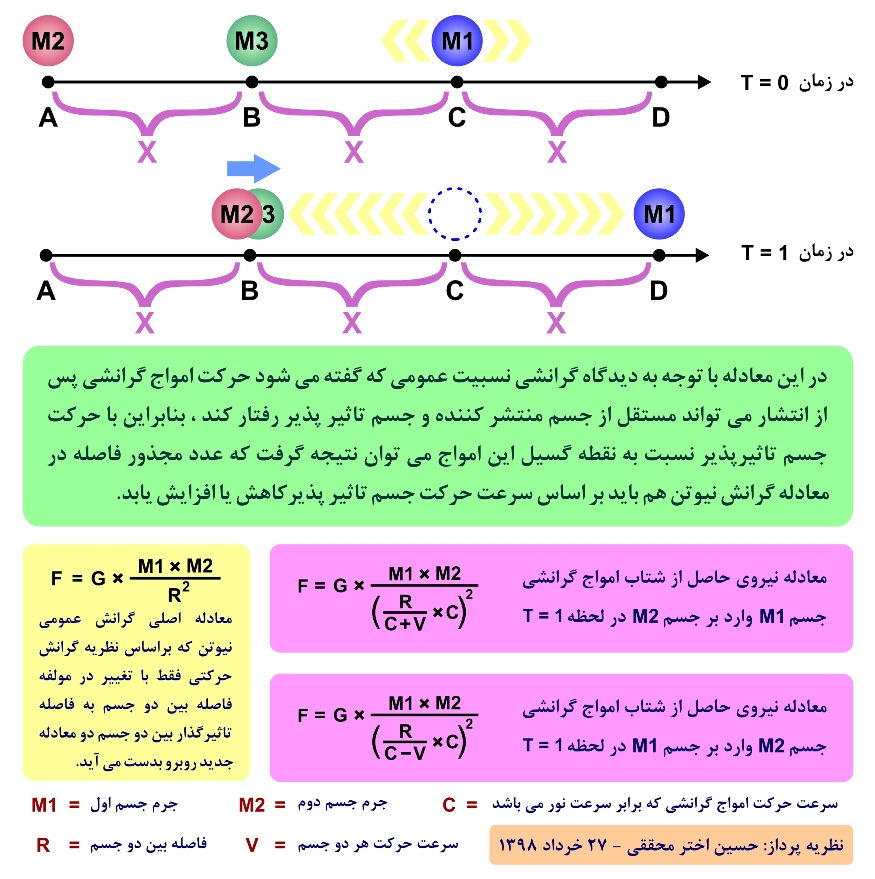
A description of the modified Newton gravitation equation based on the theory of motion gravity:
According to Newton's general gravitational equation, the component F is equal to the gravitational acceleration force on both M1 and M2 bodies, which is the same for both objects, and the component G is equal to the universal gravitational constant of Newton, and M1 is the mass of the first object and the mass M2 The second object and R are equal to the distance between the two objects M1 and M2.
In the still state of the two M1 and M2 objects, Newton's general gravitation law works correctly without any correction, and it is correct. But when at least one of the two M1 and M2 objects begin to move, and especially at high speeds, the general gravitation equation Newton has some distortion in the calculations obtained over observations, and the main reason is that the Newton gravity equation expresses the velocity of the gravitational force infinitely, instantaneously and instantaneously, and thus the movement of at least one of The two bodies M1 and M2 should not change the force of gravitational acceleration, which in Einstein's view, as well as observations of astronomy The present and many other documents of this case, namely, the instantaneous and instantaneous effect of gravitational force, are completely rejected and are considered for velocity of velocity of gravitational velocities and are considered in the range of velocity of light motion in a vacuum, which according to the same principle in theory The motion of gravity, the velocity of the M1 and M2 bodies, enters into the general Newton gravitation equation, and provides two different equations with respect to the position of motion of each of the two objects, which in addition to the previous components in The main equation of gravitation of Newton, two other components called V, whose constant velocity of motion of bodies M1 and M2, as well as the component C, C) Gravitation in space, which is approximately equal to the velocity of light in a vacuum. In these two new equations, we want to know that the distance traveled by the target object, or the object of gravity, until the gravitational waves arrive at the space How much will be around it, in these two equations, is the only difference being the existence of a positive or negative sign in the equation that the choice of this sign is due to the position of each object relative to the other object in the direction of movement of both objects in front or rear Another object is determined.
In these two equations, if according to the direction of motion of both objects, the target object (the object of gravitational acceleration), which is in the first equation of the object M2, moves towards the gravitational waves of another object, here the body of M1 In this case, the desired sign is positive and if the target object (the object of gravity gravitational force), which is in the second equation of the object M1, is removed from the gravitational waves released from the other object, here the object M2, then the desired mark Will be negative. Given the hypothesized velocity of the gravitational velocity velocity and the velocity of the object, if the distance between two objects, R, is divided into this hypothesized velocity, then the time required to reach gravitational waves from the moment of propagation to the moment of reaching The space around the target object is obtained, and as a result, if this time is multiplied by the actual velocity of the gravitational wave, C is multiplied by R, or, in other words, the distance from the motion of the object and the motion of the gravitational waves is obtained for moving objects, The amount of force generated by the gravitational acceleration depends on the effective component R, rather than the component R. It should also be noted that in this equation, the velocity of motion of gravitational waves is assumed to be based on the velocity of light motion in a vacuum, which requires accurate calculation of its actual value.